Fleas are blood-sucking parasites of humans and animals found all over the world. Approximately 30 species of fleas call Missouri home, the most common of which are the cat flea. Fleas occur in great abundance, cause an irritating bite and can transmit disease.
Biology & Life Cycle
The entire life cycle of a cat flea is approximately 20 to 35 days, and is highly dependent on ideal conditions of temperature (85 degrees F) and moisture (85% humidity). Temperatures below 55 degrees F stunt development. Flea reproduction takes place indoors year round, but outdoor is limited to warm weather months in Missouri.
Four stages comprise the life cycle of fleas: egg, larva, pupa and adult. Adult fleas can remain in the at the pupa stage until they detect a suitable host, which can occur over months. They are very patient pests! This behavior is one reason fleas are often discovered by people returning home after a long vacation or moving into a new home where hungry adult fleas have been waiting inside a cocoon without access to hosts.
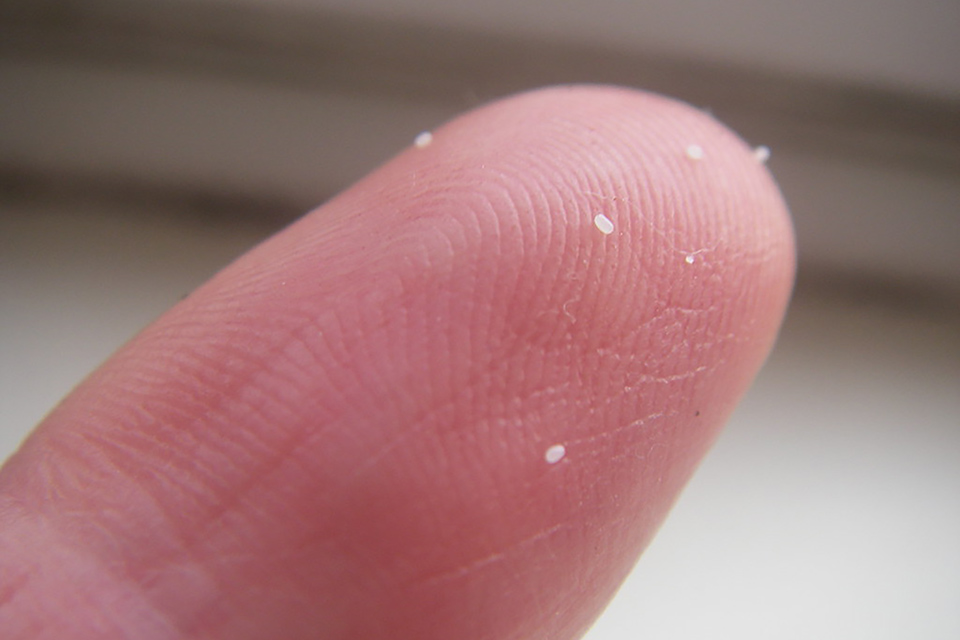

Habitats in Missouri
Diet & The Search for Food
The mouth of fleas is adapted for puncturing animal skin and sucking blood. Both male and female fleas suck blood. Fleas normally prefer the blood of domestic animals over that of humans, so it is not unusual for people to coexist with their pet and its flea population under normal conditions and be bitten only occasionally. However, when the preferred host is absent (likely, your pet!), a population of hungry adult fleas will accumulate. Hungry fleas will not discriminate between blood from pets and other animals and will attack almost any warm-blooded animal that strays near.
Cats and dogs scratch and bite themselves constantly when heavily infested. As a result, their skin is irritated and their coats become rough and unkempt. The initial irritation, itching and rash are caused by salivary secretions injected by the flea during feeding.
Several diseases may be transmitted by the bite of an adult flea, including plague and typhus. Rodents and pets are the most common sources of fleas and the diseases they carry. Flea voracious feeding behavior and their indifference of hosts increase the potential for fleas to transmit disease-causing organisms between humans and animals.
Request a Free Pest Inspection
Some description text for this item
Request a Free Pest Inspection
Some description text for this item
Management & Eradication
Please visit the University of Missouri’s Fleas webpage for more information about fleas.

